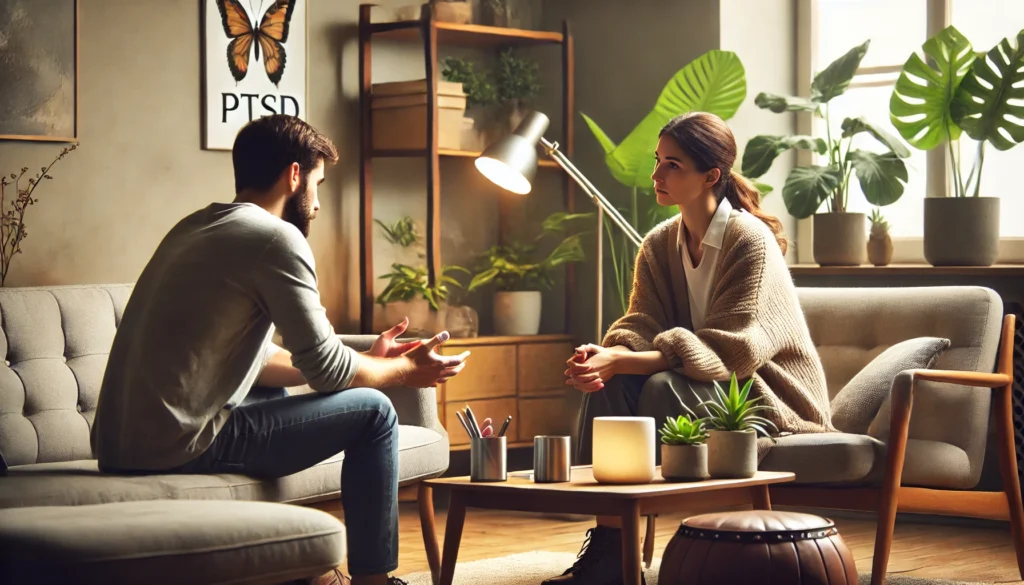
Trauma is a complex and deeply personal experience that can have lasting effects on an individual’s mental and physical well-being. For some, these effects evolve into long-term challenges, such as Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Understanding the link between trauma and PTSD is crucial for mental health professionals and researchers to develop effective treatment strategies.
Recognizing the connection between trauma and PTSD helps shape a more compassionate and informed approach to mental health care. By focusing on both the psychological and physiological impacts of trauma, professionals can offer better support. Further, survivors can feel more empowered as they understand their experiences and the potential pathways to healing..
Defining Trauma
Trauma occurs when an event overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope. It can manifest as either physical or psychological trauma. Physical trauma includes visible injuries, while psychological trauma stems from deeply distressing events. Both types can disrupt an individual’s sense of safety and control, leaving long-term effects on their well-being.
Types of Psychological Trauma
Psychological trauma can be categorized into three types, each varying in intensity. Acute trauma is triggered by a single event, such as a car accident or assault. Chronic trauma results from prolonged exposure to harmful experiences like domestic violence or bullying. Complex trauma arises from repeated, interconnected traumatic events, often starting in childhood.
From Trauma to PTSD
Trauma does not always lead to PTSD, but for some individuals, the effects of trauma evolve into this disorder. PTSD involves several symptoms, including intrusive memories, nightmares, and flashbacks of the traumatic event. It also leads to avoidance behaviors, where individuals attempt to steer clear of trauma reminders. Negative thoughts, such as guilt or shame, are common, as is heightened arousal, like irritability and difficulty sleeping.
Risk Factors for Developing PTSD
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing PTSD after trauma. The severity and duration of the traumatic event are key, with prolonged exposure leading to higher risks. Direct involvement in the trauma, rather than just witnessing it, also increases vulnerability. Individual differences, such as genetic predisposition, previous mental health issues, and socioeconomic factors, play a role as well.
Social support is another important factor. Individuals without a strong support system may experience more severe symptoms after trauma. Understanding these risk factors helps tailor prevention and treatment strategies.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention aids with reducing the long-term impact of trauma. Survivors who receive timely therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), are less likely to develop chronic PTSD. Creating safe spaces and offering coping strategies also helps individuals begin their healing journey.
Treatment Options for PTSD
PTSD can be debilitating, but there are several effective treatments that offer hope for recovery. Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT) helps individuals process traumatic memories and develop healthier coping strategies. Another effective treatment is Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), which targets emotional distress related to trauma and helps reduce its impact on daily life.
Medication is also a common treatment for PTSD, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like sertraline and paroxetine. These medications can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall mood. In addition to traditional therapies, complementary treatments such as yoga, meditation, and art therapy can promote emotional resilience and aid survivors in reconnecting with their bodies. These holistic approaches complement more conventional therapies, contributing to a comprehensive recovery process.
Emerging Research
Ongoing research is uncovering new possibilities for treating PTSD. Neurofeedback therapy is one promising approach that helps regulate brain activity to restore emotional balance. Psychedelic-assisted therapy is also gaining attention, with controlled use of substances like MDMA showing potential in trauma processing. Additionally, AI-driven therapies are being developed to recognize and manage PTSD triggers in real-time, offering personalized care to survivors. These innovations are paving the way for more effective, tailored treatments.
Related Articles:
What to Expect During an IV Therapy Session
How to Manage Asthma Symptoms During Allergy Season
Beyond Cholesterol: The Hidden Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease
Surgical Versus Non-surgical Bunion Treatment: Which is Right for You?